 |
|
| Home | |
| Victor Hess | |
| Auger Project | |
| Coord.systems | |
| Terrestrial | |
| Galactic | |
| Celestial | |
| Space weather | |
| Unix Time | |
| Projects | |
| Ask me | |
| Contact | |
The daring balloon flights of Victor Hess
|
As you have seen in the previous animation
of the balloon flight Victor Hess used several instruments
for taking the essential data that lead to the discovery of cosmic rays.
|
|
|
An electroscope is an instrument for quantifying the magnitude of electric charge present. Figure 1 shows a classical electroscope with "metal leaves" made of gold or aluminum, Once a charged probe is moved close to the metal disk, the metal leaves move apart. Assume a positive charge is close to the metal disk. This would involve the induction of negative charges on the metal disk, the metal rod and at the metal leaves. Like charges cause repulsive Coulomb electrostatic forces. |
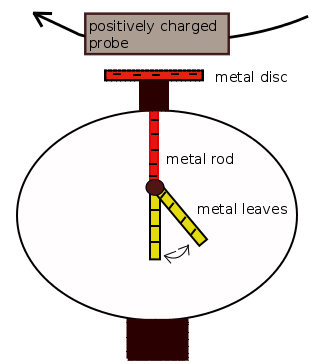
Figure 1: Electroscope
|
|
Electroscopes measure radiation of charged particles and radiation which causes the production of ions (ionizing radiation due to radioactive decay). |
|
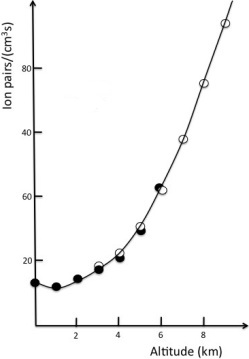
Figure 2: Experimentally determined ionization rate as function of altitude
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:HessKol.jpg |
When Hess made these balloon flights up to an altitude of 5300 m he measured increasing radiation levels higher in the atmosphere. At about 5 km altitude he detected significantly higher levels of radiation compared to the radiation at sea level. Cosmic rays are composed of charged particles which produce new ions upon interaction with molecules at relatively high altitudes in the atmosphere. Due to these collisions with air molecules at higher atmospheric altitudes cosmic ray particles loose kinetic energy. A large percentage is finally absorbed by air molecules relatively close to ground level. |
|
His measurements also reveal that the level of radiation decreases up to an altitude of 1 km before rising again due to cosmic rays. The radioactive decay of radon and further radioactive chemical elements which occur in the soil cause higher levels of radiation close to the Earth's surface.
|
|
|
Venturing a balloon flight during an almost total eclipse Hess could exclude the Sun as the radiation's source for these particularly high-energy cosmic rays. The Sun is a source of low energy cosmic rays. He concluded that ultra-high-energy cosmic rays enter the atmosphere from outer space. For the groundbreaking results of his meticulous work Victor Hess was awarded the Nobel prize for physics in 1936. |

Figure 3: Victor Hess before one of the balloon flights
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Nobel_Prize.png http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Hessballon.jpg |